Alloy
A substance having metallic properties and being composed of two or more chemical elements of which at least one is metal.Alumina
The chemical compound aluminum oxide. A ceramic used in powder or rod form in thermal spraying operations. May also be used as an abrasive grit blasting medium.Anode
The electrode maintained at a positive electrical potential.Arc
A luminous discharge of electrical current crossing the gap between two electrodes.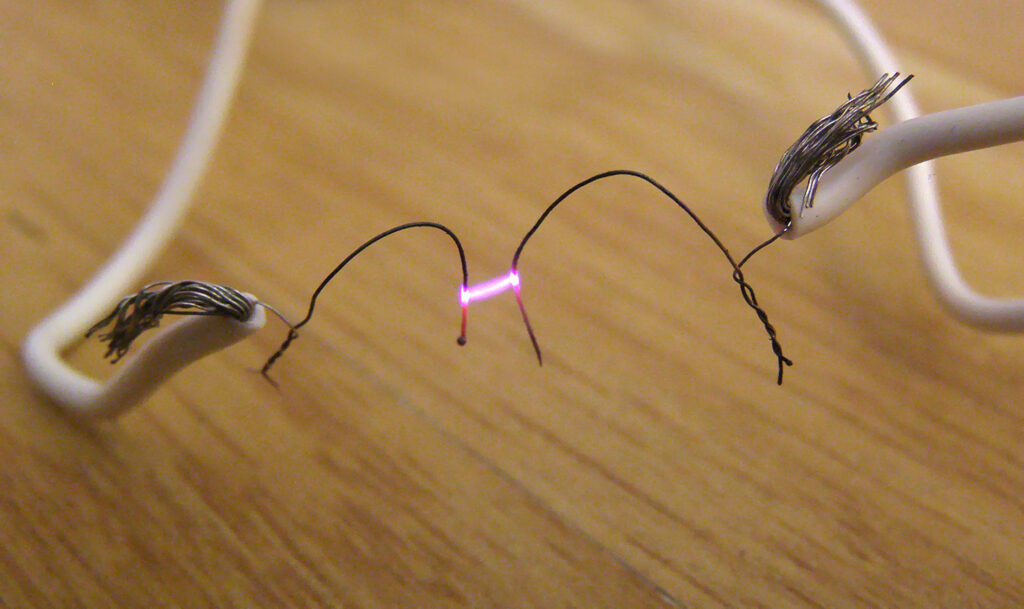
Arc gas
The gas introduced into the thermal spraying arc chamber and ionized by the arc to form a plasma gas.Arc spraying
A thermal spraying process using an arc between two consumable electrodes of surfacing materials as a heat source and a compressed gas to atomize and propel the surfacing material to the substrate.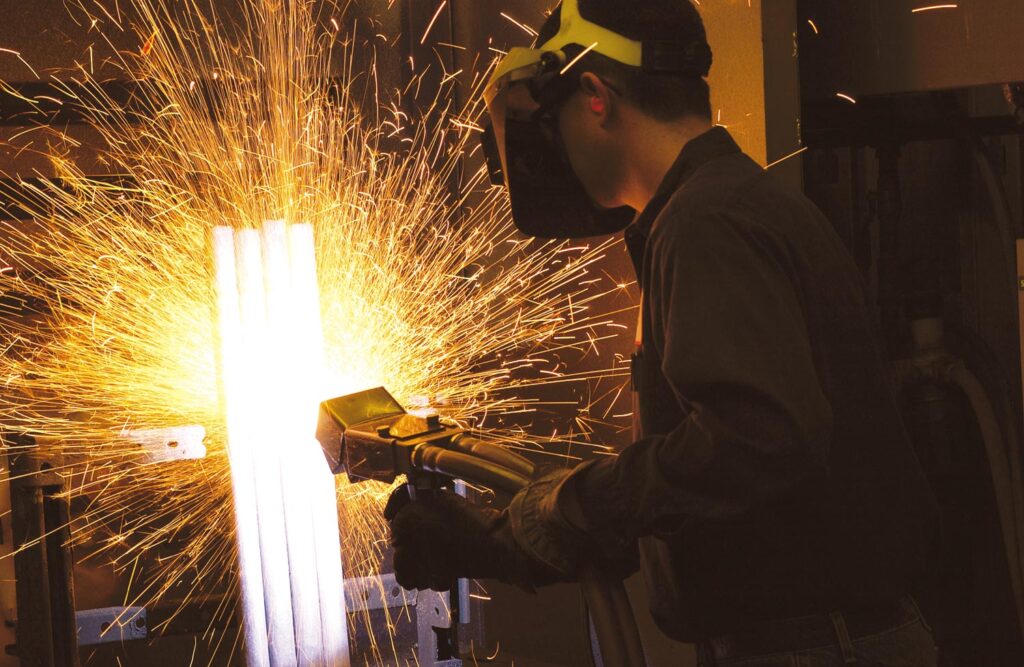
Atomization
Production of a fine spray of liquid particles.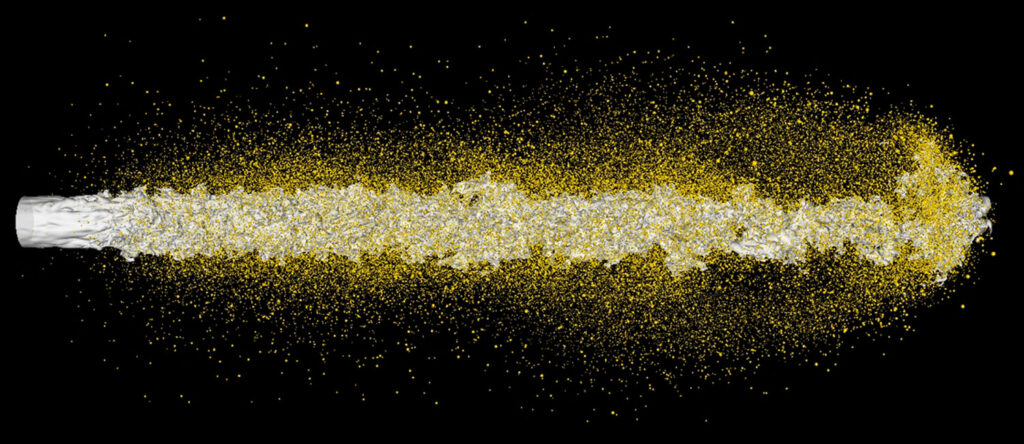
Bond coat
A preliminary (or prime coat) of material that improves adherence of the subsequent spray deposit.Bond strength
The force required to pull a coating free of a substrate, usually expressed in kPa (psi).Carbide
A chemical compound formed between carbon and a metal or metals, such as tungsten carbide, tantalum carbide, titanium carbide, and chromium carbide.Carrier gas
The gas used to carry powdered material from the powder feeder or hopper to the thermal spray gun.Cathode
The electrode maintained at a negative electric potential.Cermet
A physical mixture of ceramics and metals, such as alumina plus nickel, and zirconia plus nickel.Composite coating
A coating consisting of two or more dissimilar spray materials which may or may not be layered.Delamination
A situation in thermal spray where a coating segment breaks away from the substrate due to stresses and/or poor surface preparation. Also, a process in waterjet stripping where the coating is fractured by the high pressure water and large coating particles spall off the substrate.Deposition efficiency
The ratio, usually expressed in percentage, of the weight of thermal spray deposit to the weight of the material sprayed.Deposition rate
In thermal spraying, the weight of material deposited in a unit of time.Dispersant
Additive that increases the stability of a suspension of powders in a liquid.Dwell time
The length of time the spray material is exposed to the heat zone which produces and sustains a molten condition.Flame spraying
A thermal spraying process in which an oxyfuel gas flame is the source of heat for melting the surfacing material. Compressed gas may or may not be used for atomizing and propelling the surfacing material to the substrate.Flow meter
A device for indicating the rate of gas flow in a thermal spray system.Gradated coating
A thermal spraying deposit composed of mixed materials in successive layers which progressively change in composition from the constituent material lot the, substrate to the surface of the sprayed deposit. Also referred to as graduated or graded coating.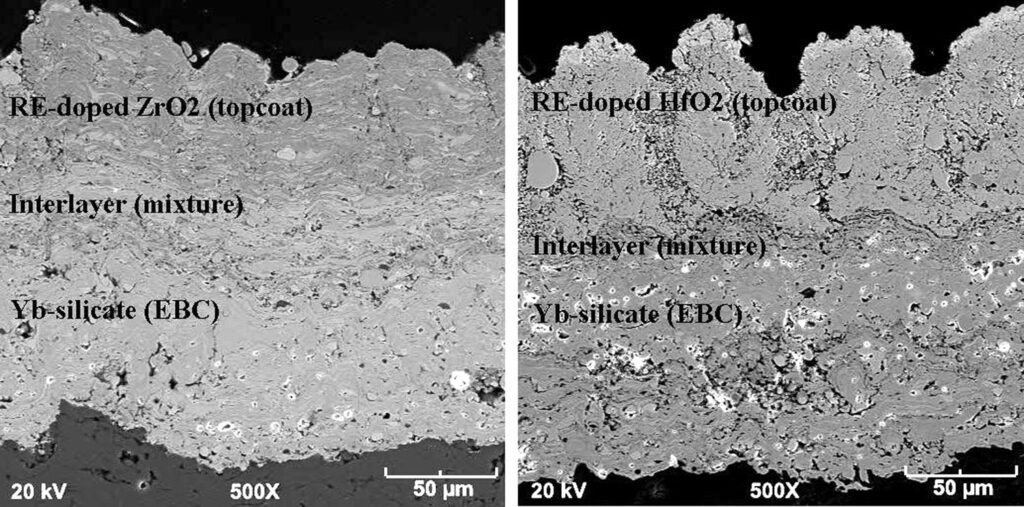
High efficiency particulate air (HEPA) filter
An air filter that removes 99.97 percent of all particles larger than 0.3 microns.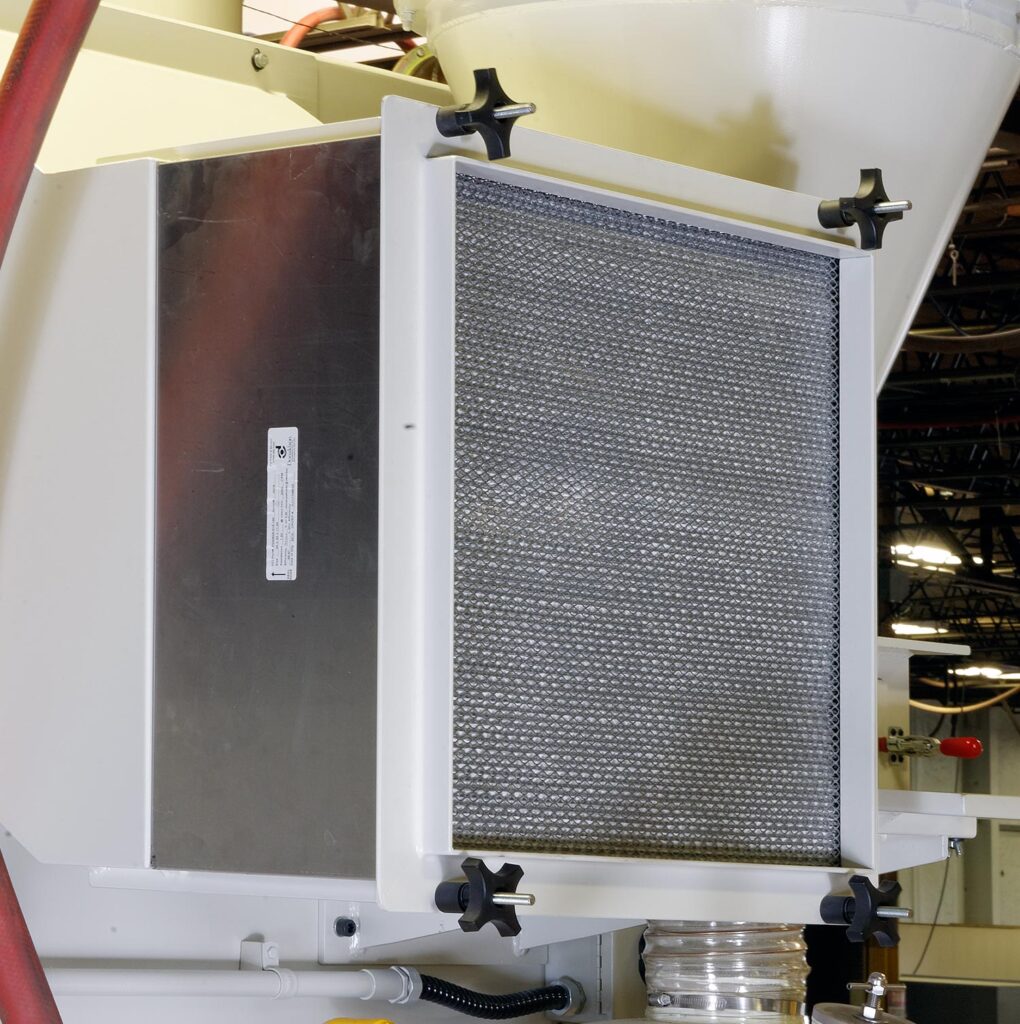
Overspray
The excess spray material that is not deposited on the part being thermal sprayed.Oxide
A chemical compound. The combination of oxygen with a metal forming a ceramic, such as aluminum oxide, zirconium oxide.Plasma spraying
A thermal spraying process in which a nontransferred arc is utilized as the source of the heat that ionizes a gas, which melts and propels the coating material to the workpiece.Porosity
Cavity type discontinuities within a thermal sprayed coating.Primary gas
The major constituent of the arc gas fed to the thermal spray gun to produce the plasma, usually argon or nitrogen.Secondary gas
The minor or second constituent of the arc gas fed to the thermal spray gun to produce the plasma.Shadow mask
A protective device that partially shields the area of work, thus permitting some overspray to produce a feathering at the coating edge.
Solution precursor plasma spray (SPPS)
A thermal spray process where a liquid feedstock solution is heated, precipitated and then deposited onto a substrate.Spalling/spallation
The flaking or separation of a sprayed coating.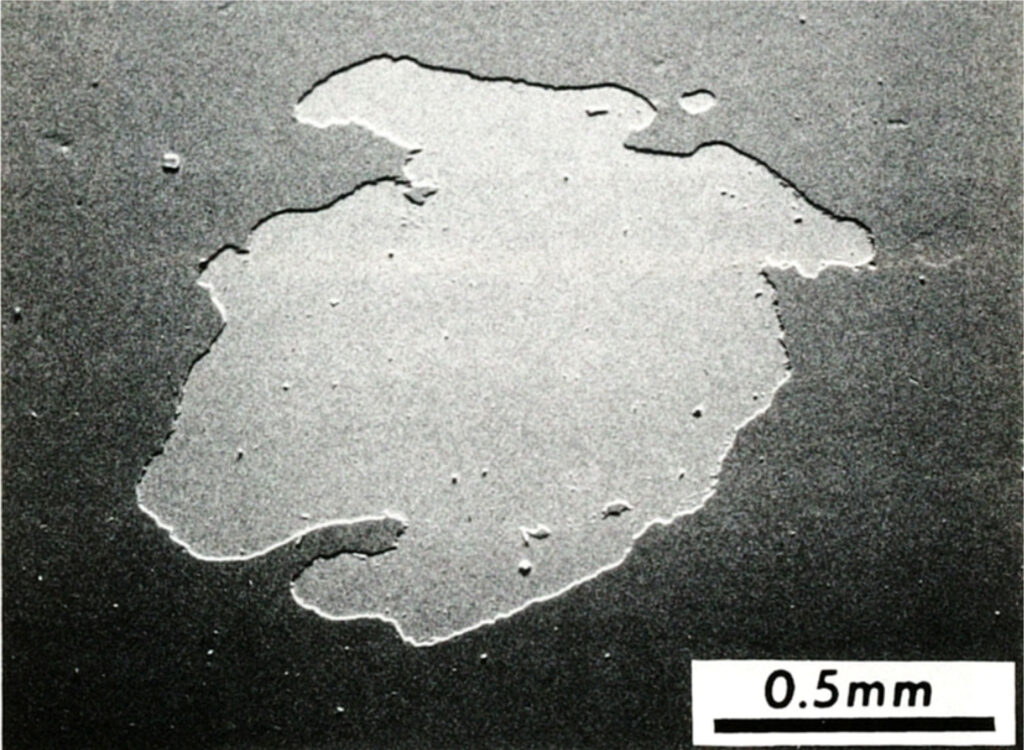
Suspension plasma spray (SPS)
A form of plasma spraying where a fine powder (normally <10 micron or submicron) is dispersed in a liquid suspension before being injected into the plasma jet.
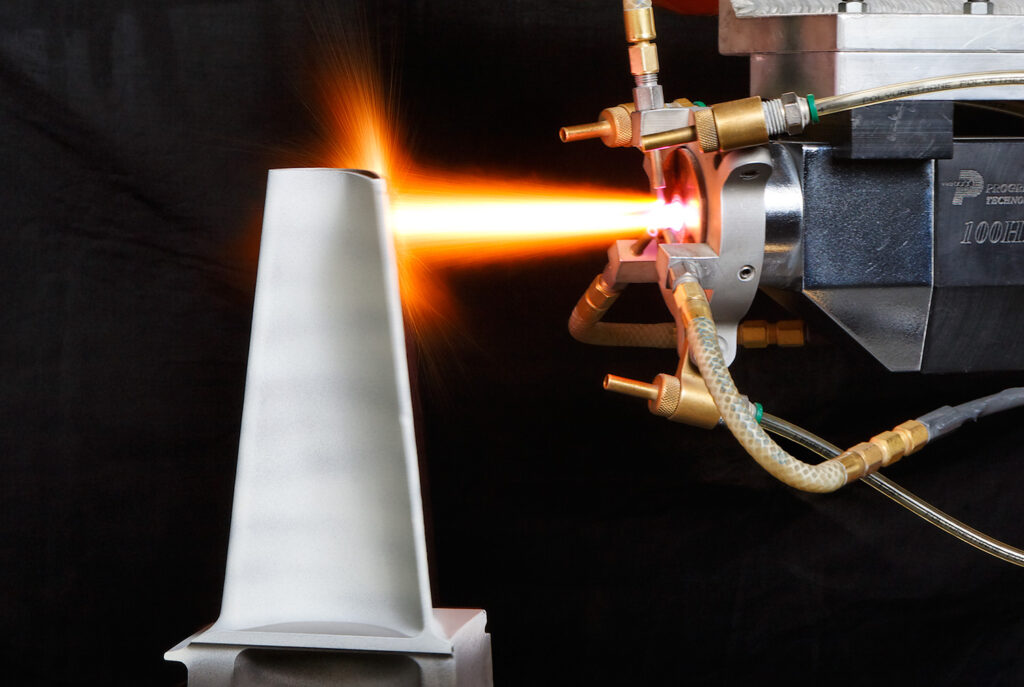
Thermal spraying
A group of processes in which finely divided metallic or nonmetallic surfacing materials are deposited in a molten or semi-molten condition on a substrate to form a spray deposit. The surfacing material may be in the form of powder, rod, cord, or wire.